Resources
31 August 2021
It is easy to say you are holding an awareness month, but let’s consider the why, what and how.
24 August 2021
This article examines the guidance available for school leaders, proprietors, governors, staff and practitioners to help them better support children and young people with bladder and bowel issues as they return to school.
01 August 2021
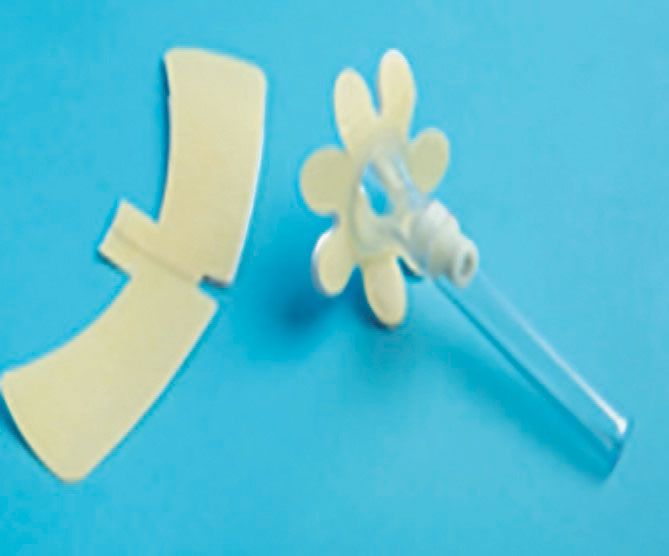
Urinary incontinence is prevalent in men, with 61% of the general population of men experiencing lower urinary tract symptoms. These symptoms present as problems with voiding, storage or post-micturition of urine. Even after assessment and treatment, some men are still left with urinary incontinence, which is normally managed or contained by either pad products or urinary catheters (if clinically indicated). However, there is a vast range of alternative devices for containment. This article reviews some of the alternative devices that are available, namely sheaths, body worn urinals and penile compression clamps. It discusses the merits and disadvantages of each device and advises when they should or should not be used.
19 July 2021
It is estimated that one in 12 children and young people in the UK suffer with a wetting or soiling problem, which can have a devastating impact on their family life, social life and self-esteem. Left untreated, bladder and bowel problems can cause serious health complications, but with the right treatment and support most children can overcome their problem or learn to manage it. This article outlines what ERIC, The Children’s Bowel & Bladder Charity, can do to help.
30 June 2021
‘Urinary incontinence is among the most common paediatric problems and it is commonly assumed to resolve with age. Consequently, parents and clinicians often adopt a ‘wait and see’ approach. A significant proportion of children, however, continue to suffer from persistent urinary incontinence into adolescence. This article describes the development of a smartphone app to aid adherence to bladder training in young people with urinary incontinence.
25 June 2021
Indwelling urinary catheters are still one of the most commonly used invasive devices in health care, with recognised significant risk factors, including catheter-associated urinary tract infection (CaUTI) and sepsis. Timely and successful removal of the catheter often falls to the responsibility of community nurses. There has been much debate about the optimum timing and circumstances for a successful trial without catheter (TWOC). This article looks at best practice guidelines and relevant clinical evidence to support healthcare professionals in making choices around TWOC procedures.
21 June 2021
World Continence Week (WCW), taking place from 21–27 June, is an annual health campaign run by the World Federation for Incontinence and Pelvic Problems (WFIPP). The campaign highlights the impact that urinary incontinence can have on people’s lives and encourages sufferers to seek help to improve their quality of life.
03 June 2021
Current Covid restrictions have forced many healthcare professionals to embrace technology and work in very different ways. Indeed, the traditional telephone has allowed the Newcastle continence service to provide a service to patients referred with all types of urinary incontinence. But, is it even possible to assess someone’s continence and devise a treatment plan over the telephone?
27 January 2021
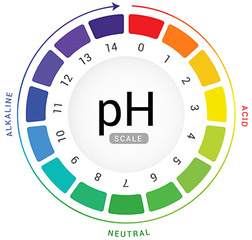
The maintenance of skin pH is essential if it is to provide a barrier to the outside world. This article examines how skin pH is maintained normally, what can disrupt it and the consequences of change. Finally, best practice guidance on restoring and maintaining a healthy skin pH and barrier function is provided.
04 November 2020
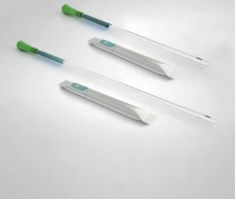
As a clinician, it is important that you are aware of the latest products and innovations that have the potential to improve outcomes for you and your patients. Each month, UCCT will highlight a product that is new, improved or innovative in order to keep you up to date.
Here, we present GentleCath™ Glide, a hydrophilic urinary catheter that uses FeelClean™ Technology to facilitate smooth, fast and convenient intermittent catheterisation.
Here, we present GentleCath™ Glide, a hydrophilic urinary catheter that uses FeelClean™ Technology to facilitate smooth, fast and convenient intermittent catheterisation.

.jpg)